Category: Lake and River Fronts
“Plastics and Lake Erie” a forum on Tues Dec 4, 2018

Tuesday December 4, 2018 at 7:00 pm
“Plastics and Lake Erie”
The flyer is here
The video is here
Rocky River Library, 1600 Hampton Rd, Rocky River 44116
Moderated by Elizabeth Miller, Environmental Reporter, Ideastream
Panelists:
Jill Bartolotta, Extension Educator, Ohio Sea Grant College Program
Crystal M.C. Davis, Policy Director, Alliance for the Great Lakes
Erin D. Huber, Executive Director and Founder, Drink Local Drink Tap

Elizabeth Miller
Co-sponsored by the Sierra Club, Case Western Reserve University Siegal Lifelong Learning Program, League of Women Voters-Greater Cleveland, Cleveland.com, Ideastream, Rocky River High School Environmental Club and Bay Village Green Team
Corporate sponsor: First Interstate Properties, Ltd.

Oral Histories of the 1969 Cuyahoga River Fire by Rebekkah Rubin, Belt Magazine
“The Myth of the Cuyahoga River Fire” from Science History Institute
The Myth of the Cuyahoga River Fire
The blaze that sparked the modern environmental movement . . . or did it?
Click here to read

Wastes, Water, and Wishful Thinking: The Bttle of Lake Erie by Arnold W. Reitze Jr. 1968
Wastes, Water, and Wishful Thinking: The Bttle of Lake Erie by Arnold W. Reitze Jr. 1968
City Planning Commission adopts new plan for East Side lakefront greenway Plain Dealer April 14, 2016
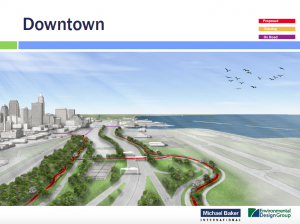
http://www.cleveland.com/architecture/index.ssf/2016/04/city_planning_commission_adopt.html
CLEVELAND, Ohio – The city’s Planning Commission on Friday voted unanimously to adopt a plan for an East Side lakefront greenway loop with new connections to neighborhoods.
Proponents characterized the plan as “unsexy” and “meat and potatoes,” but also as pragmatic and achievable.
“We wanted something that could be built in our lifetimes, or at least our work lifetimes, and not so expensive that it couldn’t be built,” said Bobbi Reichtell, executive director of Campus District Inc., one of the community development organizations that led the study.
The plan aims to improve access to a stretch of waterfront walled off from Lake Erie by the I-90 Shoreway, the lakefront railroads and Burke Lakefront Airport.
Generally, the East Side lakefront is less accessible and has less high-quality public space than the West Side, which boasts Edgewater Park.
The plan is an attempt at addressing that imbalance, and to follow up on ambitions outlined in the city’s 2004 Waterfront District Plan, but on a relatively tight budget.
The $24.5 million plan calls for creating 8.1 miles of greenway paths along North and South Marginal roads, with connections to North Coast Harbor to the west and the lakefront marinas and Gordon Park to the east.
The Planning Commission voted unanimously to adopt the plan, making it the city’s official vision, and eligible for funding.
Likely sources of money would include federal programs that could provide cash by 2021 at the earliest, said Michelle Johnson, a director at Akron-based Environmental Design Group, which co-authored the plan with the Cleveland office of Michael Baker International, an engineering firm.
“The implementation is obviously going to be incremental,” said Freddy Collier, the city’s planning director. “The city will be working in tandem with others to explore financial possibilities wherever possible.”
A key portion of the plan depends on moving the chain-link fence on the south side of Burke Lakefront Airport three feet to the north to improve the existing Lakefront Bike Path on North Marginal Road.
Today, the path varies from 6 to 10 feet in width, but because it’s right next to the fence, the usable width is narrower, the plan said. Hydrants also exist in the middle of the path, making it dangerous.
Johnson said the plan calls for moving two 800-foot-long sections of the fence three feet to the north.
“We are very supportive of this project to identify and overcome those barriers to the development,” Pat Singleton, chief of business development and management at the city’s Division of Port Control, said about moving the fence.
She said the division, based on the newly approved plan, would apply to the Federal Aviation Administration for permission to move the fence.
Other portions of the plan call for creating a new pedestrian and bike bridge across the I-90 Shoreway to North Marginal Road at East 40th Street, plus a similar bridge from the city’s Municipal Parking Lot at East 18th Street to South Marginal Road.
The bridges alone would account for nearly half of the cost of the plan.
Developer Fred Geis, a member of the Planning Commission, said he’d like to see the greenway loop finished as a single project, instead of having the city build a collection of small segments as small pots of money become available.
He criticized the patchwork approach to completing the Cleveland section of the Towpath Trail in the Cuyahoga Valley, which intersperses completed and incomplete sections.
“It changes every year, and the street markings can’t keep up.”
He praised the new lakefront plan as “super necessary.”
“It’s an ambitious plan,” he said. “I really hope you get it done from stem to stern.”
Lake Erie aggregation

Bill Roberts
1 PBS Newshour 8.3.2014 about Lake Erie Algae Blooms
2 Lake Erie from Cleveland Historical
4 Lake Transportation from the Encyclopedia of Cleveland History
6 Saving Lake Erie Short Documentary from National Geographic
7 Environmentalism by David Beach written in 1997 for Encyclopedia of Cleveland History
8 Great Lakes Area of Concern from Wikipedia
Lake Erie Documentaries/Video
“Emerging Routes to Environmental Activism: Lake Erie Sportsmen and the League of Women Voters” by Terrianne Shulte D’Youville College Excursions Journal 2011
“Emerging Routes to Environmental Activism: Lake Erie Sportsmen and the League of Women Voters” by Terrianne Shulte D’Youville College Excursions Journal 2011
Lake Erie from Cleveland Historical
Lake Erie from Cleveland Historical
